Manage ruby versions with direnv
If you are not a ruby developer, a ruby version manager might be overkill if you only need it from time to time.
direnv is a tool that manages your environment depending on the current
directory1. At first, I started using it to manage environment variables
for specific projects. After that, it replaced version managers for languages
I use less often, like python and javascript (node). Once my projects had
everything neatly configured in .envrc files, it made sense to include the
ruby version as well.
How?
$ brew install direnv
First, install direnv and configure your shell to use it.
$ brew install chruby
Then install chruby2, but do not configure your shell to source it.
Instead, we will do this via direnv. Edit ~/.direnvrc and append the
following:
source /usr/local/opt/chruby/share/chruby/chruby.sh
# Uncomment to use with rubies installed with ruby-build:
# RUBIES+=(~/.rbenv/versions/*)
# use ruby [version]
use_ruby() {
local ver=$1
if [[ -z $ver ]] && [[ -f .ruby-version ]]; then
ver=$(cat .ruby-version)
fi
if [[ -z $ver ]]; then
echo Unknown ruby version
exit 1
fi
chruby $ver
}
If your ruby versions are not in ~/.rubies, uncomment the RUBIES line and
set the value appropriately.
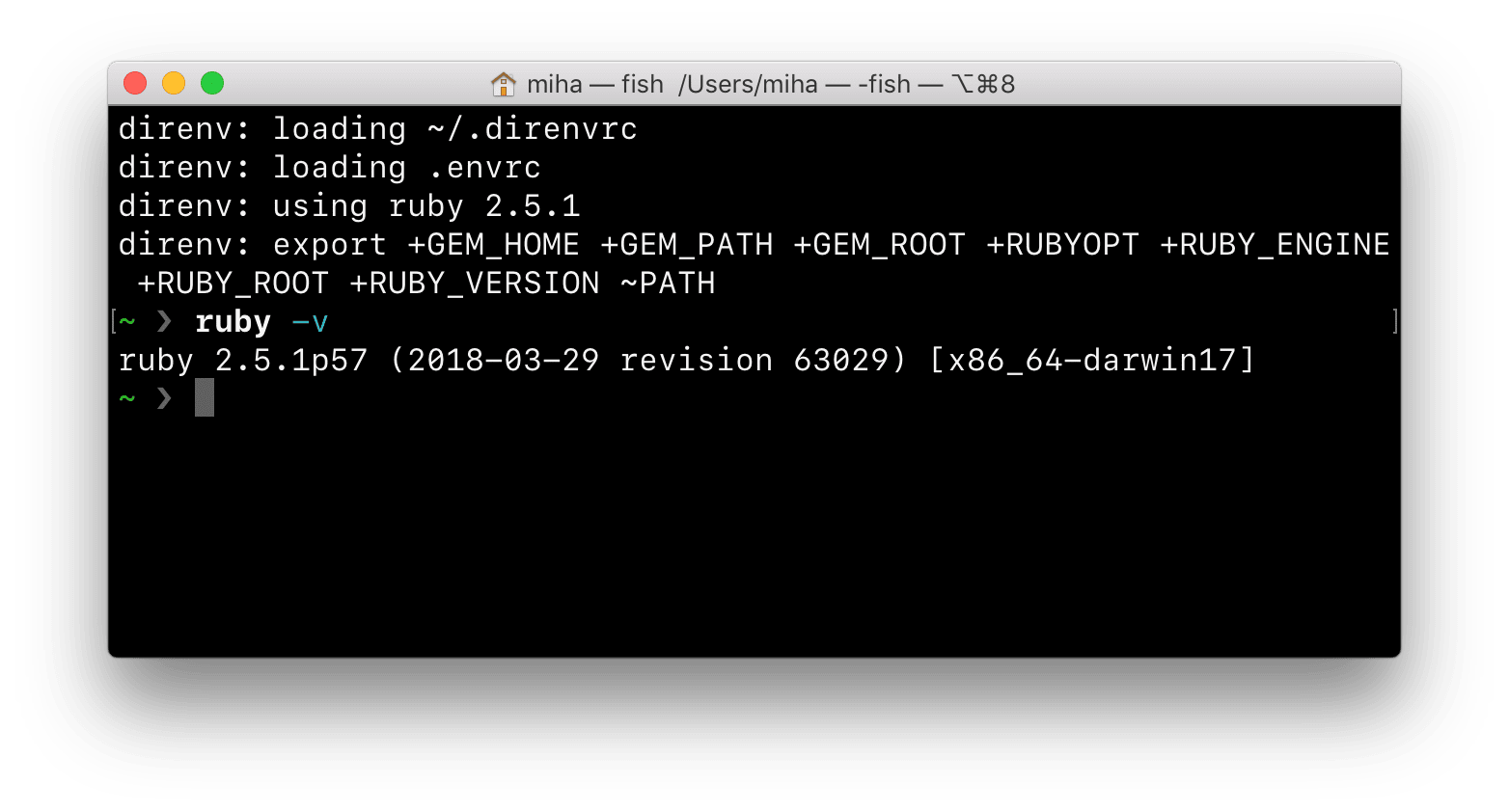
Relaunch your shell, navigate to your project, run direnv edit ., and add
the following (assuming you have 2.5.1 installed):
use ruby 2.5.1
Your shell should now be ready with the specified ruby version.
See also: Manage project dependencies with direnv.